Target 2: Semang Dike Project by GlobalMin Ventures
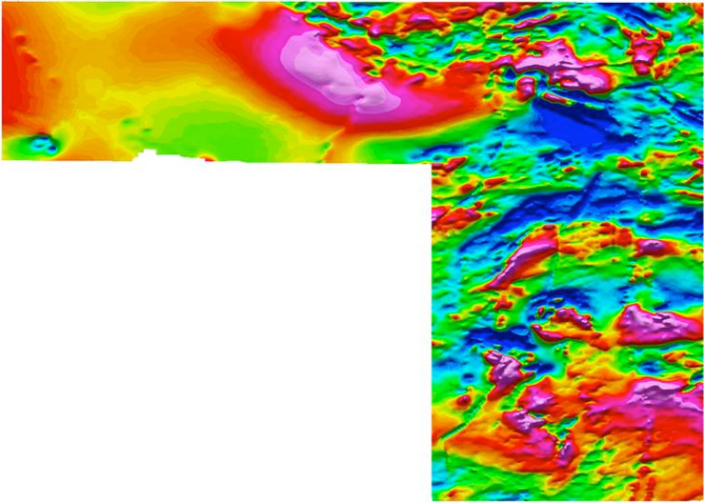
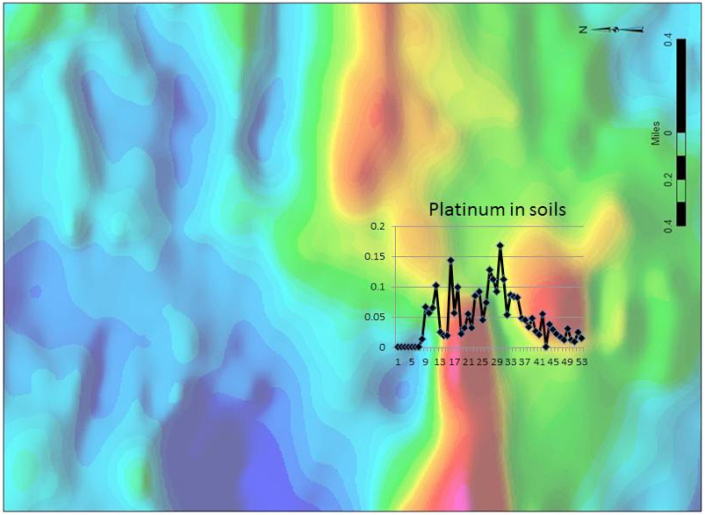
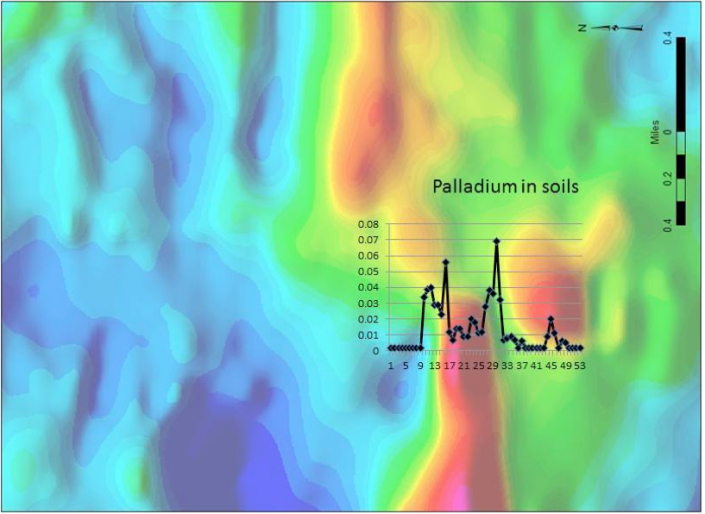
The Semang dike is a large topographic feature in north central Guyana, striking N-S and crossing the Mazaruni River. The Mazaruni River sediments downstream of the dike contain anomalous PGMs and related elements, which led to reconnaissance sampling of dike rocks and soils in the two places where access is easiest by boat. Both areas contain rocks and soils anomalous in Pt-Pd-Au and related elements like Cu-Ni-Co. Airborne magnetics, flown after the geochem sampling, indicate that soil geochem anomalies become strongest as the lines approach airmag highs. Additional soil and rock sampling is now planned to extend the lines into areas of additional, strong airmag highs.
The dike is approximately 25 miles long and may be as wide as one mile, based on topography, and is mapped as Avanavero age of 1.6 to 1.8 Ga. Whole rock data suggest that the western arm of the dike is different from the eastern arm, the western portion being more chemically evolved and less primitive. This may be explained by the two arms not being comagmatic, or that different vertical levels of a comagmatic dike are being sampled, indicating that a degree of differentiation has taken place during cooling.
Interpretation and Conclusions of the Sampling Program
Target 2 at Semang is a large mafic dike that is clearly mineralized with PGMs, with the potential to host a large tonnage deposit because of its sheer size. Exploration is incomplete along most of the Semang dike where multiple aerial magnetic anomalies define additional prospective zones.
Our Exploration Plan
Target 2 is the Semang dike, a large body of mafic rock approximately 25 miles long in a N-S direction and 1 mile wide. Mazaruni River sediments downstream of the dike contain elevated Pt-Pd. Anomalous concentrations of Pt-Pd and related elements have been found in Semang dike rocks and saprolitic soils overlying the dike in several places. Ground geochemistry was initiated before the aerial geophysical survey was flown, and it is now apparent that Pt-Pd concentrations increase along survey lines as they approach areas of highly magnetic rocks as shown by the aerial survey.
Several zones of highly magnetic rocks occur in and around the Semang dike and these areas will now be the focus of additional ground geochemistry. Anomalous zones will be drilled once the ground geochemistry is complete. Core drilling of holes that are 500 to 1000 feet deep will probably be required to adequately assess the nature of the PGM mineralization that is just now being detected in this large dike. Whole rock and trace element geochemistry suggests that differentiation has taken place during cooling of the dike magma and this subsequent igneous layering must be characterized through drilling in order to develop an understanding of the location, geometry, and strength of this PGM mineralization.
Semang Dike Exploration Data
The following images show the thoroughness with which our exploration program determined that Semang Dike is a good target for further exploration.